Heat Transfer Fluid: Necessary for Maximizing Industrial Heating & Cooling Equipments
Heat Transfer Fluid: Necessary for Maximizing Industrial Heating & Cooling Equipments
Blog Article
The Function of Heat Transfer Fluid in Enhancing System Performance and Safety
In the ever-evolving landscape of industrial procedures, warm transfer liquids (HTFs) emerge as pivotal parts in enhancing both system performance and safety. These specialized liquids, understood for their superior thermal conductivity and regulated viscosity, allow reliable warm exchange, which is essential for structured operations. Nonetheless, the impact of HTFs expands beyond plain efficiency; their inherent thermal security and low flammability considerably add to risk mitigation. As markets face the need for high-performance and risk-free procedures, comprehending the nuanced duty of HTFs becomes vital. Yet what exactly makes HTFs so necessary in today's commercial structures?
Understanding Heat Transfer Liquids
Heat transfer fluids, often thought about the lifeline of thermal monitoring systems, play a crucial role in managing temperature throughout various commercial applications - heat transfer fluid. Industries such as chemical processing, power generation, and production count on heat transfer liquids to ensure devices runs successfully and safely.
The selection of a suitable heat transfer fluid is important to the success of a thermal monitoring system. In summary, a comprehensive understanding of heat transfer fluids is vital for optimizing system performance, making sure functional safety and security, and attaining cost-effective thermal management solutions.
Secret Characteristic of HTFs

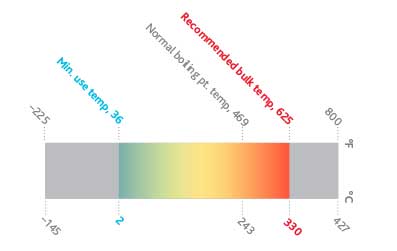
The specific heat capability of an HTF defines the quantity of warmth power required to alter its temperature, affecting just how successfully the system can respond to temperature variations. The boiling and freezing points of HTFs additionally play a pivotal role, especially in systems subjected to extreme temperature levels, making certain liquid security and preventing phase changes during operation.
Enhancing System Performance
To improve system performance with warm transfer liquids (HTFs), it is necessary to integrate a comprehensive approach that thinks about both fluid buildings and system layout. The option of an ideal HTF is crucial, as its thermal conductivity, thickness, and details warmth ability straight impact the effectiveness of warm exchange. High thermal conductivity guarantees rapid heat transfer, while optimum thickness assists in smooth flow through the system, reducing energy consumption. In addition, a high details warmth capability enables the visit fluid to store and move even more thermal power, improving overall system efficiency.
Just as crucial is the style of the heat transfer system itself. Designers need to ensure that parts such as warm exchangers, pumps, and piping are made to enhance the residential properties of the chosen HTF. For circumstances, the area and material of warmth exchangers should be enhanced to take full advantage of warmth transfer effectiveness. The combination of innovative technologies, such as variable speed pumps and clever surveillance systems, can significantly enhance the responsiveness and flexibility of the system to changing operational conditions.
Boosting Operational Safety And Security
Making certain operational security in heat transfer systems needs a careful focus on both the residential or commercial properties of heat transfer liquids (HTFs) and the layout and maintenance of the entire system. HTFs should possess thermal security, low flammability, and ideal thickness to reduce dangers such as leaks, fires, and system malfunctions. Picking the ideal HTF is critical as it identifies the system's capacity to manage temperature level changes without compromising safety.
The design of the system need to include redundancies and fail-safes to handle prospective hazards efficiently. This consists of the combination of safety shutoffs, stress relief devices, and temperature level tracking systems to spot and address abnormalities immediately. Routine maintenance is important to ensure that all parts, including pumps, pipes, and seals, are working properly and are without wear or deterioration, which might lead to unsafe leaks or failings.
In addition, workers responsible for the procedure and upkeep of heat transfer systems have to be adequately educated in safety methods and emergency feedback treatments. Consistent training programs and safety and security drills can considerably reduce the probability of accidents, ensuring next a much safer working environment. Eventually, a comprehensive technique to safety-- incorporating fluid choice, system layout, and workforce training-- is indispensable for ideal operational protection.
Industry Applications of HTFs
Commonly utilized across different sectors, warm transfer liquids (HTFs) play a crucial function in boosting the efficiency and dependability of thermal administration systems. In the chemical sector, HTFs are integral for maintaining exact temperature levels throughout responses, ensuring product consistency and high quality. They assist in warmth exchange procedures in reactors, condensers, and heat exchangers, thus enhancing energy usage and decreasing waste.
In the oil and gas field, HTFs are used in both upstream and downstream operations. They manage temperature in drilling operations and improve effectiveness in refining processes by offering steady thermal conditions. This results in decreased downtime and improved security, especially in important procedures such as purification and splitting.
The renewable resource field likewise profits substantially from HTFs, especially in concentrated solar power (CSP) plants. Here, HTFs transfer captured solar power to power generators, making it possible for efficient electricity generation. The pharmaceutical industry depends on HTFs for specific temperature level control in both synthesis and storage space, making sure product efficacy and safety.

Furthermore, the food and beverage field uses HTFs for pasteurization, sterilization, and cooking procedures, enhancing both item security and production performance. Throughout these industries, HTFs act as vital elements in maintaining ideal operational efficiency and security.
Conclusion
Heat transfer liquids are necessary in enhancing commercial system efficiency and safety by supplying high thermal conductivity, ideal viscosity, and thermal security. Proper option and upkeep of HTFs enhance warmth exchange effectiveness, therefore increasing Homepage functional efficiency. The reduced flammability of these fluids is crucial for lessening risks and making certain risk-free procedures. Comprehensive workers training and regular upkeep further sustain the reliability and efficiency of industrial processes, strengthening the essential duty of HTFs in varied applications.
Report this page